The silent metamorphosis: decoding aging and evolution of arteries
The arterial network of the human body, which extends over almost 100,000 kilometers, plays a vital role in our well-being and health. For healthcare professionals, a thorough understanding of the structure of the arteries, how they change with age, and the impact of disease and behavior on these vessels is essential.
Artery structure: a complex design
Arteries are made up of several layers, each with a specific function. The innermost layer, the intima, is in direct contact with the blood. The medial layer, or media, is composed mainly of smooth muscle cells and elastic fibers, giving arteries their elasticity and ability to withstand the high pressure of blood pumped by the heart. Finally, the adventitia, the outer layer, provides additional structural support.
Proteins such as elastin and collagen play a key role in the structure and function of arteries. Elastin enables arteries to stretch under the pressure of blood, while collagen gives them strength and elasticity.
This elasticity enables the vessels to absorb some of the energy generated by cardiac ejection, preventing excessive flow from damaging vital organs and the finest vessels.
The pathophysiological mechanisms behind arterial aging
This arterial compliance decreases with age - this is arteriosclerosis or arterial stiffness - but it is also impacted by numerous factors: genetic, pathological or behavioral (smoking, sedentary lifestyle, diet, medication...) and increases the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular complications by inducing both structural and functional changes in the vascular wall (1).
Typical aspects include progressive stiffening of the blood vessel wall due to endothelial dysfunction, proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC), changes in extracellular matrix (ECM) composition (including elastin fragmentation and increased collagen production), increased oxidative stress, lipid accumulation and inflammation.
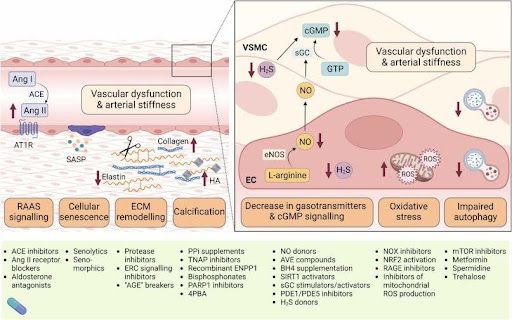
The main pathophysiological mechanisms involved in vascular dysfunction and arterial stiffening are explained in this publication (1) and illustrated in this diagram, which also outlines possible therapeutic strategies.
With vascular aging, the aorta loses its cushioning function, leading to an increase in pulsatile pressure, further aggravating endothelial dysfunction and arterial stiffening.
The aorta plays an important role. Thanks to its elastic properties, it will dampen the pulsatile pressure resulting from the heart's contraction, thus maintaining continuous blood flow to the arterioles (3). This property is known as the Windkessel principle. Importantly, endothelial dysfunction and arterial stiffness are independent risk factors for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality (4).
Arteries therefore play a crucial role in blood circulation and overall health. Understanding their complex structure, the natural aging process and the effects of disease and behavior on these vessels is fundamental for any healthcare professional.
This knowledge not only helps to identify the risks of cardiovascular disease, but also offers opportunities for prevention and therapeutic strategies to maintain the health and functionality of arteries throughout life.
That's why integrating pOpmètre® into your practice is crucial. Fast to use, non-invasive and non-operator dependent, it will be an essential ally in cardiovascular assessment and prevention for your patients.
You know the age of your arteries, and now you can measure it!
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36738307/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568163723002817?via%3Dihub
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.hyp.37.5.1236
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12588755/, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11358934/, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28923899/, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36736671
